REAPER has a VU Meter plugin called ‘JS: VU Meter’ that you can use to measure an audio track’s average loudness. JS: VU Meter features the classic VU Meter appearance and displays RMS (Root-Mean-Square) loudness and the peak of whatever audio signal you route through it.
VU Metering In REAPER
The process of gain staging a track can be a total frustration if you do not have the proper tools.
Something that I love about REAPER is its detailed design of the VU meter as well as its functionality.
REAPER’s ‘JS: VU Meter’ is another one of many reasons why I always come back to REAPER!
In this detailed look at the REAPER VU meter, I will show you what it is, what it does, and how you can use it for staging gain in your track.
JS: VU Meter
First, let’s look at JS: VU Meter and what it shows us.
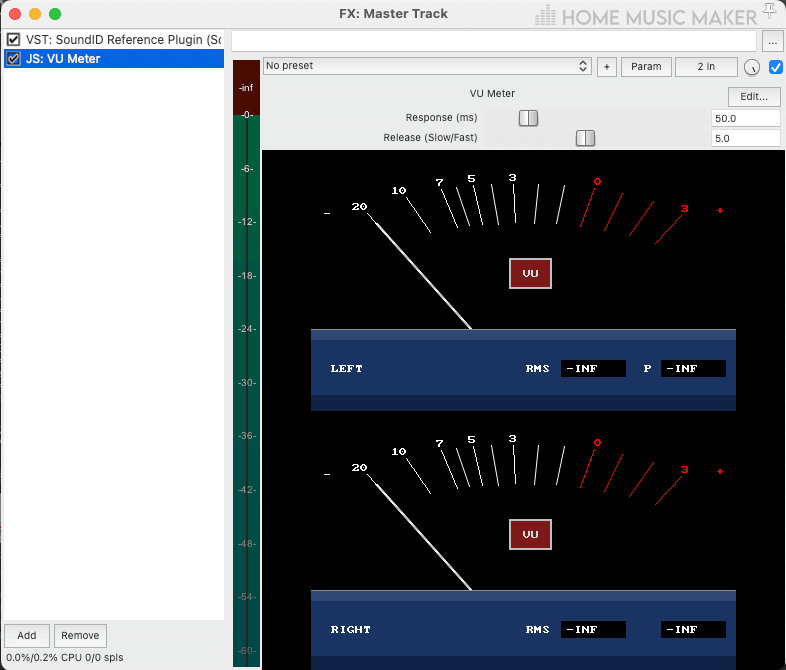
As you can see, JS: VU Meter has a straightforward design and visual display. Here is a list of the features that make up JS: VU Meter:
Response (ms): This knob lets you control how quickly JS: VU Meter responds to the incoming audio signal.

Release (Slow/Fast): This knob lets you control how quickly JS: VU Meter stops responding to the incoming audio signal.

Visual display meter: This is the graphical display of JS: VU Meter. This meter will display the loudness of an audio signal in real-time.
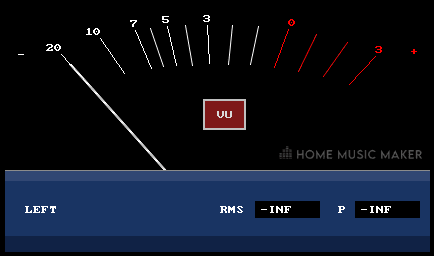
Left and right channel: You will notice that the regular JS: VU Meter plugin has two separate meters for the left and right sides of your stereo field. The ‘(Summed)’ version of JS: VU Meter only has one display because it consolidates the left and right channels into one single channel.
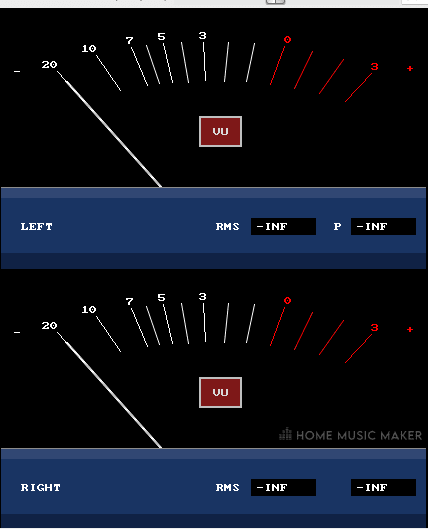
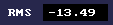
RMS box: This box shows us the RMS (Root-Mean-Square) loudness of any audio signal we route through the VU Meter. RMS loudness is average loudness measured within the ‘Response’/’Release’ window you set.
Peak box: This box shows us the peak loudness of any audio signal we route through the VU Meter.
JS: VU Meter gives REAPER users access to an effective VU Meter without a bunch of unneeded features.
Inserting The REAPER VU Meter
To insert the REAPER VU Meter onto a track, simply press the ‘Show Track FX Window’ button on the desired track, locate JS: VU Meter, and double-click it to insert it onto your track.
This works for any track within your REAPER project, including the master track or any BUSS tracks.
Using The REAPER VU Meter
Using the REAPER VU Meter is as easy as inserting it onto a track and observing/analyzing what it tells you.
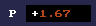
The REAPER VU Meter shows us RMS (Root-Mean-Square) loudness and Peak (P) loudness.
You can use the REAPER VU Meter to see if your track is clipping and its average volume/peak. This information can help you with your gain staging, mixing, and mastering.
What Is The Difference Between The Standard and ‘Summed’ Version of JS: VU Meter?
The only difference between the standard and ‘summed’ version of JS: VU Meter is that the standard plugin has a display for both the left and right channel of your stereo field, and the summed version only has one.
Both plugins tell you the same thing: the JS: VU Meter (Summed) consolidates the left and right audio channels into one single channel.
This can make reading it a bit simpler, but you lose some of the detail.
What Does VU Meter Stand For?
VU meter stands for ‘Volume Unit Meter.’
You use a VU meter to measure the output level of an audio signal. VU meters used to be only analog audio equipment, but DAWs (Digital Audio Workstations) all feature a digital VU meter.
What Do VU Meters Measure?
A VU Meter measures the output level of an audio signal based on either peak or RMS loudness.
The peak level is the loudest point that an audio signal reaches.
RMS stands for ‘Root-Mean-Square‘ and is the average loudness of an audio signal, usually measured in a time period of 300 ms (milliseconds).
How To Read VU Meter
You read a VU meter by playing an audio signal through it and observing its peaks and average loudness (RMS).
For example, playing an audio signal or track through a VU meter displays the loudest point in the audio (peak). It shows you where the average volume level lands (RMS).
Use the VU meter in your DAW to make educated decisions while proper gain staging.
What Is 0dB On a VU Meter?
0dB on a VU meter is also called 0 VU.
0dB/0 VU on a VU meter is the loudest point that audio can output at before it starts clipping.
Clipping can cause unpleasant distortion or other noises and is generally a big no-no in music production.
What Level Should My VU Meter Be At?
I recommend that you record audio at a level between -20dB and -6dB on your VU meter. This will give you a headroom of that amount, making your gain staging process much easier.
Recording audio at a reasonable level on the VU meter allows you room to further process the audio while mixing and mastering.
REAPER Change VU Meter Color
Unfortunately, the only way to change the color of the VU meter in REAPER is to switch to a theme with a different colored VU meter.
Here is another article on REAPER Themes that you can use to find some cool themes that might have a different colored VU meter.
Although you can change the color of almost every track in REAPER, you can not change the color of the master track or VU meter.
Do VU Meters Affect Sound Quality?
No, VU meters only help you measure the level of an audio signal.
Audio engineers use them during the gain staging, mixing, and mastering process.
VU meters do not do anything in the way of affecting the sound of something in your track.
Should I Mix With a VU Meter?
Yes, a VU meter is essential for audio and music production.
Using a VU meter during the gain staging, mixing, or mastering process is vital.
You use a VU meter to monitor the output level of an audio signal. Without a VU meter, you will have difficulty knowing the overall volume of your track and if you are experiencing any clipping.
Is VU The Same As RMS?
No, not exactly.
VU stands for ‘Volume Unit,’ and you will typically find it in the phrase ‘VU Meter.’ You use a VU Meter to measure the volume of an instrument or track. You can usually measure this volume level based on peak or RMS.
RMS stands for ‘Root-Mean-Square‘ and is just a measurement of an audio signal’s output loudness.
Related Questions
Does Every Digital Audio Workstation Have a VU Meter?
Yes, you will have a VU meter at your disposal, whether you use FL Studio, Pro Tools, Studio One, etc.
A VU meter is a very standard device in audio/music production.
What Is an Analog VU Meter?
Unlike a digital VU meter that is a part of your DAW, an analog VU meter is a piece of actual hardware.
An analog VU meter is typically only used in high-end studios that can afford a setup with a bunch of audio hardware gear.
In my opinion, there is no real advantage of using an analog VU meter over a digital one.
Is the VU Meter a New Technology?
No, not at all.
Audio engineers/music producers have been using VU meters for recording and gain staging purposes pretty much since the dawn of recording.
Although VU metering was a fully analog process back in the day, it is still relatively the same as now despite the digital switch.
Is a Third-Party VU Meter Plugin Something Worth Investing In?
I think there is no point in spending money on a third-party VU Meter plugin.
This is because REAPER, and almost any other DAW for that matter, will have a VU Meter or VU Meter plugin that comes with it. I think there are much better things to spend your money on in the world of music/audio production than a fancy VU Meter plugin.
Check out this article to learn more about gain staging in REAPER.

 Want to connect with other music producers for help and guidance?
Want to connect with other music producers for help and guidance?