KEY TAKEAWAYS:
The quality of your audio can be affected while bouncing due to factors such as normalization, dithering, file format, and equipment quality. To prevent it from happening, remember only to use tools like dithering and normalization when necessary and always export to a high-quality format.
Mixdown Mysteries
Mixing and producing music can be a complex and time-consuming process. But it’s essential to take the time to get the mixdown right.
Bouncing a mix is the final step before sharing it with the world. But many factors can affect the sound of a bounced mix.
This post will look at the most critical factors when bouncing a mix, including dither, normalization, audio file format, audio interfaces and drivers, and playback devices and software.
Considering these factors, you can ensure that your mix sounds its best when others hear it.

Factors That Can Affect A Bounced Mix’s Sound
The Role Of Dither In Mixdowns
Dither is an often-overlooked but crucial aspect of the mixdown process. With it, your mix may avoid quantization errors. This can make it sound harsh and less dynamic.
Understanding when and how to apply dither in the mixdown process is essential. Generally, it’s best to apply dither when converting from a high bit depth to a lower bit depth.
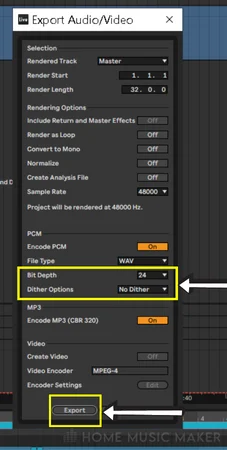
Also, it would help if you used a high-quality dither algorithm. This provides the best noise shaping for the audio being processed.
The Importance Of Proper Normalization
Understanding The Concept Of Normalization
The concept of normalization is to bring the peak level of the audio signal to a specific level. Usually, a maximum level is -0.1dBFS (decibels relative to full scale) or -1dBFS.
During the normalization process, the software analyzes the audio signal. And determines the highest peak level. Then it adjusts the audio signal level so that the highest peak is at the desired level.
How Normalization Affects The Loudness Of A Mix
Normalization affects a mix’s loudness by adjusting the audio signal’s level. This can result in a more consistent listening experience across different playback devices. But it can also have some adverse effects on the mix.
Best Practices For Normalizing A Mixdown
Normalization is a powerful tool that can improve the listening experience and make the mix sound more consistent across different playback devices. But it should be used with caution to avoid any adverse effects.
Instead of normalizing to a peak level, use a loudness metering plugin. It will measure the loudness of the mix in LUFS (Loudness Units relative to Full Scale). This will help you adjust the mix’s loudness without compromising the dynamic range.
Audio File Format Considerations
Choosing The Correct File Format For Your Mixdown
When it comes to bouncing a mixdown, it’s essential to consider the audio file format that will be used. Different file formats have other characteristics and trade-offs that can affect the sound quality of the mix.
Understanding The Trade-Offs Between Lossy And Lossless Formats

The two most common audio file formats are lossy and lossless. Lossy file formats, such as MP3 and AAC, remove some audio data to reduce the file size.
This can result in a lower audio quality. But the smaller file size can help share and stream online.
Lossless file formats like WAV and FLAC keep all the audio data. This results in higher audio quality, but the larger file size can be an issue for sharing and streaming online.
How Do Sample Rate And Bit Depth Affect Audio Quality?
Sample rate and bit depth are essential factors that affect the quality of audio recordings. They determine the resolution and dynamic range of the audio signal.
The sample rate is the number of times the audio signal is sampled per second, measured in Hertz (Hz). A higher sample rate means more audio signal samples are captured per second.
Resulting in a higher resolution and a more accurate representation of the audio. Standard sample rates include 44.1kHz, 48kHz, and 96kHz.
The bit depth is the number of bits used to represent each audio signal sample. A higher bit depth captures more information about the audio signal.
Resulting in a higher dynamic range and a more remarkable ability to capture fine details in the audio. Standard bit depths include 16-bit and 24-bit.
The Impact Of Audio Interfaces And Drivers
Understanding The Role Of Audio Interfaces In The Mixdown Process
An audio interface is a device that connects a computer to an external audio source. Such as a microphone or an instrument. It’s an essential piece of equipment for recording and producing music. And the quality of the audio interface can affect the sound quality of the mixdown.
The audio interface converts the analog audio signal into a digital signal that the computer can process.
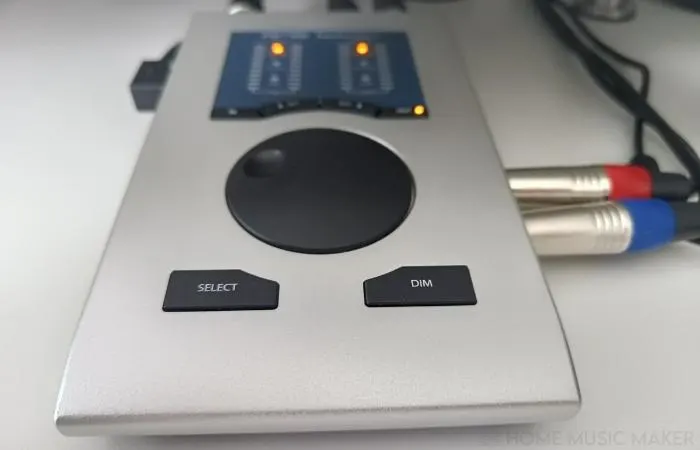

Choosing The Correct Audio Interface For Your Needs
Selecting the correct audio interface for your needs is crucial to achieving the best sound quality for your mixdown. There are a few things to consider when choosing an audio interface, such as:
Connectivity: Consider the number and types of inputs and outputs you need. It would help if you also considered whether you need more features such as MIDI connectivity or S/PDIF.
Quality of converters: Look for audio interfaces with high-quality converters for the best sound quality.
Preamps: If you plan on recording microphones or instruments, look for an audio interface with built-in preamps.
Processing effects: Some audio interfaces include built-in processing effects. These can be used to shape the sound of the audio during the mixdown process.
The Influence Of Playback Devices And Software
How Different Playback Devices Can Affect The Sound Of A Mix
Different playback devices can significantly impact the sound of a mix. This is because each device has unique characteristics and limitations that can affect how the audio is presented.
Different speakers and headphones have different frequency responses. They can present the audio differently. For example, headphones tend to have a more pronounced bass response. At the same time, speakers tend to have a more balanced frequency response.
A high-quality amplifier will produce a clean and accurate sound. In contrast, a lower-quality amplifier can introduce distortion and noise.
And a room with poor acoustics can make the audio sound muddy and unclear. A room with good acoustics can make the audio sound clear and detailed.
READ NEXT:
Using pink noise is a good trick to help with the frequency balance in your mix. For a more detailed look at this, check out our article on how to mix with pink noise.
The Impact Of Software Media Players On Audio Quality
The software media player you use to play back your mix can also impact the audio quality.
Different media players support different audio codecs. The playback quality can depend on the codecs and file formats the media player supports.
Some media players need help to handle high sample rates and bit depths. Resulting in a loss of audio quality.
Tips For Ensuring Consistent Playback Across Different Devices And Software
Ensuring consistent playback across different devices and software can be a challenge. But there are a few tips you can follow to achieve the best results:
Use a reference track to compare the sound of your mix to see if it is on par with professionals.
A metering plugin can help you to measure the loudness of the mix in LUFS (Loudness Units relative to Full Scale). This will help you consistently adjust the mixture’s loudness across different devices and software.
Test the mix on different devices and software, such as speakers, headphones, car audio systems, and media players. This will help you identify sound quality issues and make adjustments.
READ NEXT:
There is one more check for your mix that is crucial. Read more in our article on mixing in mono.
Related Questions
How Long Do Pros Take To Mix A Song?
It varies depending on the complexity of the song.
Professional mixers will spend a significant amount of time listening to the song. They also experiment with different techniques and processing effects. They make adjustments to achieve the desired sound.
This process can be time-consuming and requires great skill and experience.
Will Bouncing Audio Reduce Its Quality?
Bouncing audio, also known as rendering or exporting, is the process of creating a final mixdown of a song. It combines all the individual audio tracks into a single audio file.
Generally, bouncing audio will not reduce quality if the correct settings and techniques are used.
How Do You Get Punchy Vocals?
Getting punchy vocals can add energy and clarity to a mix. Here are a few tips on how to achieve punchy vocals:
1) Use EQ to boost the vocals’ presence frequency range (around 4-6kHz). This helps to add clarity and definition to the vocals.
2) Use compression to control the dynamic range of the vocals. This can add punch and consistency to the vocals. Try using a fast attack time, moderate release time, and a ratio of around 4:1.
3) Use saturation to add warmth and harmonic richness to the vocals. This can add punch and character to the vocals.
Does Increasing Bitrate Improve Sound Quality?
Increasing the bitrate can improve sound quality to a certain extent. But it’s not the only factor that affects sound quality.
At What Stages In The Production Process Do You Bounce Down Your Audio?
After mixing all the audio tracks, the final mix is bounced down to a stereo file. This is the final version of the audio that will be used for mastering or distribution.
Sometimes, it may be helpful to create sub-mixes of certain groups of tracks, such as drums, vocals, or instruments. These sub-mixes can be bounced down and used as individual tracks in the final mix.
After the final mix is completed, it is bounced to a stereo file and sent to a mastering engineer. This file will be used for final adjustments and preparation for distribution.
After mastering, the audio is bounced to the final format and codec used for distribution—for example, WAV, MP3, or AAC files.
Final Words
Bouncing a mixdown is crucial in music production and requires attention to detail.
The factors affecting the sound of a bounced mix include dither, normalization, audio file format, audio interfaces and drivers, and playback devices and software.
By understanding these factors and following the tips in this article, you can ensure that your mix sounds its best when others hear it.
READ NEXT:
Now that you have your mixdown let’s talk about mastering. Check out our guide on how to find a mastering engineer.

 Want to connect with other music producers for help and guidance?
Want to connect with other music producers for help and guidance?