A dedicated audio interface can improve sound quality. The three primary aspects of an audio interface affecting sound quality are digital to analog conversion, clock synchronization, and power isolation.
Does A Better Audio Interface Affect Sound Quality?
When building up your home studio, It’s easy to underestimate this simple piece of gear. After all, your computer probably already has one built in, so why shell out the extra cash if it’s not needed?
Surprisingly, these little boxes can bring many benefits and are considered necessary in most situations.
In this article, we will explain how these devices improve sound quality and why they are so important.
What Is An Audio Interface?

An audio interface is a piece of hardware that allows you to connect microphones and other input devices to your computer.
It converts the analog sound into digital data, which can then be processed and recorded by the computer.
Many audio interfaces also have multiple audio input channels and multiple audio output channels. This allows you to connect speakers and other audio devices like a mic preamp.
How Does An Audio Interface Improve Sound Quality?
There are three main ways that an audio interface can directly influence the quality of the audio are:
- Digital to analog conversion
- Clock synchronization
- Power isolation
These are all separate stages of the circuit inside an audio interface, and they are necessary for the machine to function correctly.
Digital to analog conversion is taking an analog signal, such as your voice, and converting it into a digital signal to be manipulated inside your computer.
To understand why this is such an important step, we first need to look closer at the difference between these two signal types.
Analog To Digital Conversion
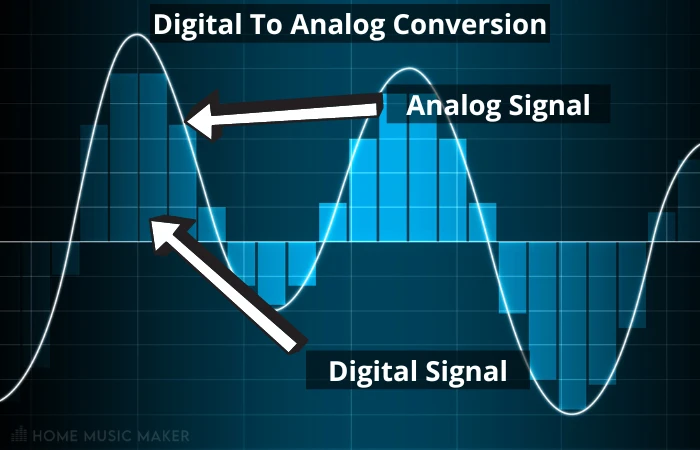
As you now know, analog to digital conversion is the process within an audio interface circuit in which an analog signal is converted to a digital signal (hence the name analog-to-conversion, also referred to as a DAC).
This is a vital part of the purpose of an audio interface and can have a considerable impact on the sound coming out the other side.
This step is so crucial because of the very nature of these two inherently different signal types.
In the analog world, we hear the sound as pressure fluctuations caused by an energy source as it propagates through the air.
Due to the nature of physics, this is known as a continuous-time signal(or analog signal).
The only problem is that analog signals are not compatible with the digital domain of computers. In the digital environment, information is represented statefully, meaning it is always in one of two states: on or off.
There is no way of storing continuous data.
The best we can do is store a representation of that signal by “sampling” the value of the signal at different time intervals.
This causes all the data between these points in time to be lost since the computer is only aware of the signal at the exact moment in time that the sampling occurs.
What happens is that we end up with a bunch of points that represent the signal that was initially a “line.” How accurate this representation is, is defined by the “sampling rate.” The lower the sampling rate, the less accurate our representation will be.
This is why a high-quality DAC is so important; a good DAC equals accurate digital audio… almost.
Clock Synchronization

It is incredible how far technology has come. But with a miniature handheld computer in the pocket of every man, woman, and child across the country, it is easy to forget how complex these machines really are.
The audio interface is no different, and the sampling performed by the DAC is only part of the story.
This brings us to something called clock synchronization.
The clock is responsible for controlling the timing of the sampling. A fast clock means fast sampling.
However, it is not uncommon for modern-day electronic systems to have multiple clocks. And since we are using two independent systems (interface and computer), more than one clock is inevitable.
Clock synchronization is when timing signals are exchanged between devices to keep them operating in sync.
In an audio interface, clock synchronization keeps the audio devices operating at the same sample rate. The audio will sound choppy and distorted if the devices are not synchronized.
The clock synchronizes the digital audio samples to be played back at the correct time. If the clock is not synchronized, the audio will sound like it is skipping or stuttering.
If only my High School Math teacher could see us now, with clock synchronization and Digital to Analog conversion, we darn near sound like we actually passed algebra 2….
*cricket, cricket, cricket*
,,, Or maybe that is just me…..
Anyway, at least we can be confident knowing our audio interface is of high quality; as we plug in the power chord with heroic posture and pride, our hearts go out to the men and women who gave…
Not so fast there. Did someone say power chord?
Because we haven’t even had time to cover the third and final process of your audio interface that directly affects the sound quality.
Power Isolation

In a perfect world, electrical signals would be stable, and algebra 2 classes would be easier to pass! However, this is rarely the case.
Electronic circuits are highly sensitive and can pick up distortion in multiple ways.
In the case of audio, what this means is poor audio quality.
Electrical noise is any unwanted signal that can interfere with the proper operation of equipment.
It can come from various sources, including power lines, electrical motors, and other electronic equipment.
This noise can degrade the quality of the audio signal, making it difficult to hear.
Certain types of electrical circuits are more sensitive to noise, just like other circuits tend to produce more noise.
One circuit that is notorious for being noisy is the power supply.
A power supply is responsible for taking the 240V(depending where you live, you may have 120V) AC “mains” power (aka the power from the wall plug in your house) and stepping it down to a stable lower DC voltage that is commonly required for most electrical components and “computer chips.”
Power isolation helps to reduce the amount of electrical noise that can affect the audio signal by using a transformer to isolate the audio signal from the power supply.
This ensures that the audio signal is not affected by any noise that may be present in the power supply, which leads to both high-quality audio and the end of all the boring technical stuff!
So now that that is over with, we can finally move on.
Even though we may look back on this day five years, ten years, or even a few hours down the road, we can rest well knowing that.. a D+ is not a passing grade. Yes, I know it’s almost there.
Still, I can not just “let you slide, bruh.” That would be unfair to the other students. You will just have to make up for it by taking summer school, end of discussion…
Er… are we still talking about audio..?
Does An Audio Interface Reduce Noise?

Some audio interfaces come with preamps that can reduce noise, but not all of them do.
Check the specs before buying if you want an audio interface with noise reduction capabilities.
Regardless though, when compared to a standard computer sound card, an audio interface will always have less noise.
An audio interface can reduce noise because it uses better quality components than a standard computer sound card. This results in less noise being produced overall.
Additionally, audio interfaces often have better shielding against electromagnetic interference (EMI). This can also help to reduce the amount of noise that is present.
Why Would I Need An Audio Interface?
If your computer does have an audio interface built in, then, more than likely, the sound quality will be poor.
This is because your computer’s built-in sound card will probably be designed for general use and not for music production.
This means that it may be lacking some of the more specialized features common to dedicate audio interfaces and helpful for audio recording and music production.
The Benefits Of Using An Audio Interface
It’s a new day, a new topic, and a new paragraph. Let us celebrate by pretending that didn’t just happen.
And as we crawl out of our cave of regret and welcome the bright, warm rays of denial shining down from above, we can finally move on to some more practical information about the real-world benefits of using a dedicated audio interface instead of the built-in interface of your computer.
Latency-Free Monitoring
Latency is the delay between the time when an audio signal enters the audio interface and the time when it is output by the audio interface.
Latency Free Monitoring is the ability to hear what you are recording in real-time without any audio latency or delay.
This is essential for recording vocal and acoustic instruments and playing your MIDI keyboard since the lag created by the audio latency is unnatural to us and makes it very difficult to keep a solid rhythm.
For example, anything over about 30ms latency is enough to make it virtually impossible for me to play my MIDI keyboard.
Phantom Power
Many microphone models require Phantom Power to function properly. This is a type of power supply that is used to power condenser microphones.
This is a big plus if you plan on recording vocals because virtually all high-quality studio microphones require phantom power.
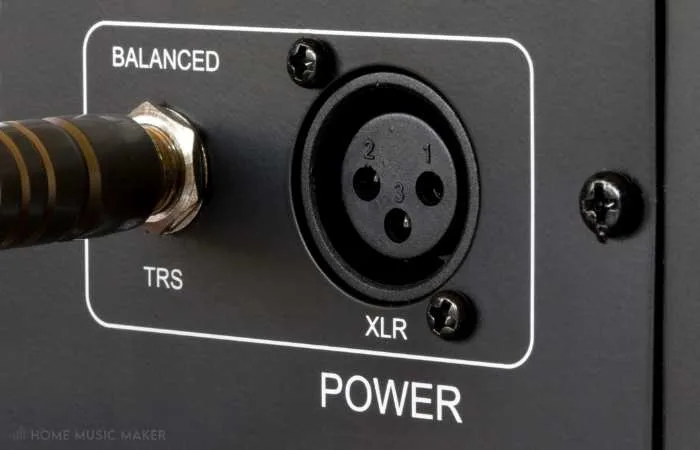

Phantom power is a DC voltage that is supplied to specific types of microphones through the audio interface. Phantom power is typically +48V. This is mainly used to power a special capacitor in the microphone that needs extra power to function.
Multiple Inputs And Outputs
This allows you to connect multiple microphones and other input devices to your audio interface. It also allows you to connect multiple speakers and other audio devices to your interface.
MIDI Connectivity

This allows you to connect MIDI devices to your audio interface. MIDI devices can include controllers like a midi keyboard and drum machines.
External IO
IO stands for inputs and outputs, and it is common for Audio Interfaces to have anywhere from 2×2 to 16×16(16 inputs and 16 outputs.
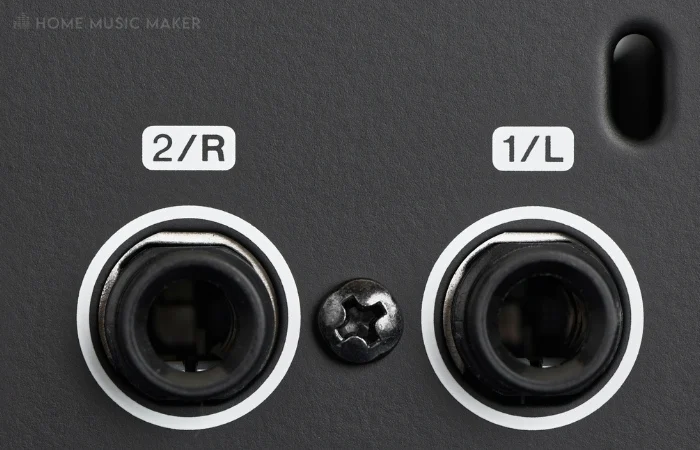

These allow you to simultaneously connect audio devices for monitoring and recording, such as headphones, preamp, effect processors, an instrument, and microphones, all essential parts of music production.
How Do I Choose An Audio Interface?
When choosing an audio interface, there are a few things you will need to consider.
1. Inputs And Outputs
You first need to consider the number of inputs and outputs you will need.
If you only plan on recording one microphone or instrument input at a time, you will only need one input.
You will need multiple inputs if you plan on recording numerous microphones or other audio input devices.
The same goes for outputs. If you only plan to connect one set of speakers or headphones, you will only need one output.
You will need multiple outputs if you plan on connecting various speakers or other audio devices.
2. Connectivity
The second thing you need to consider is connectivity.
You will need to decide how you will be connecting your audio interface to your computer. The most common options are a USB cable or Thunderbolt cable.
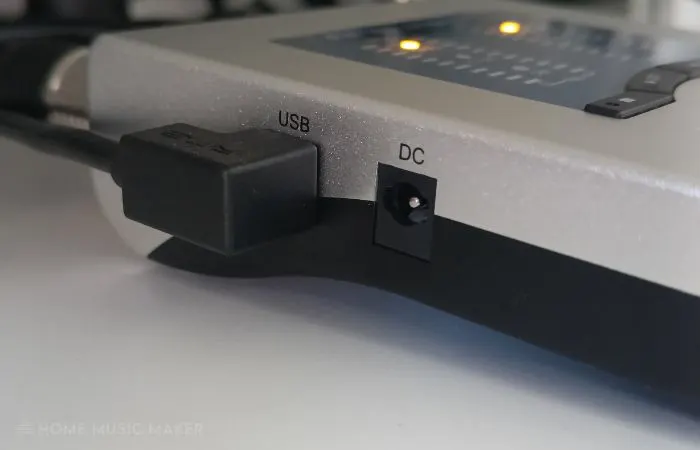

If you have a newer computer, then Thunderbolt is the better option. Thunderbolt is a high-speed connection that can carry a lot of data.
If you have an older computer, then USB is the better option. USB is a slower connection, but it is still fast enough for most audio applications.
3. Latency
The next thing you need to consider is latency.
As I mentioned earlier, latency is the delay between when the sound is created and when you hear it.
If you plan on recording vocals or live instruments, you will need an audio interface with low latency.
4. Phantom Power
The following thing to look at is Phantom Power.
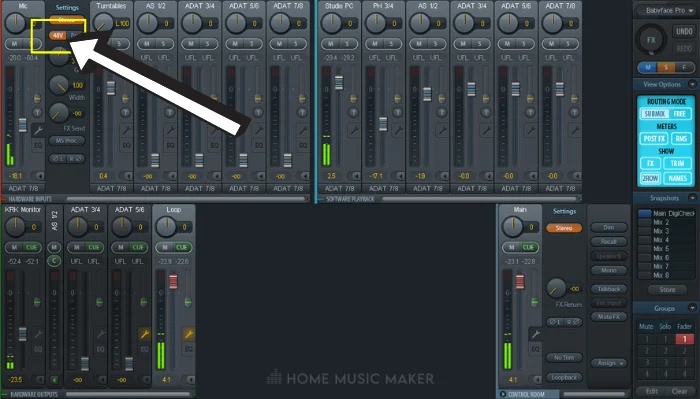
If you plan on using a condenser microphone, you will need an audio interface that provides Phantom Power.
The condenser microphone is the most common microphone type for vocals because of its superior clarity compared to a dynamic microphone.
However, most condenser microphones will only work if your audio interface can supply +48v phantom power.
5. MIDI Connectivity
The next thing you need to consider is MIDI connectivity.
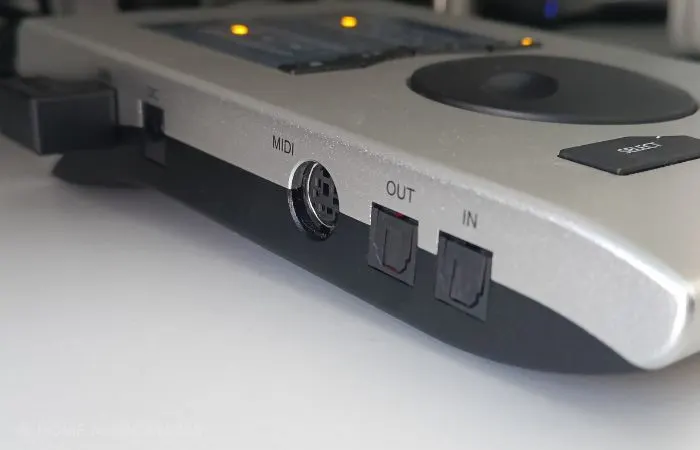

If you plan on using vintage MIDI devices, you will need an audio interface with MIDI connectivity.
Most modern-day MIDI hardware features built-in MIDI over USB. Still, if you plan on using devices that only have a standard 5-pin MIDI din connector, then you will need an audio interface that will let you interface the device with your computer.
6. Headphone Jacks
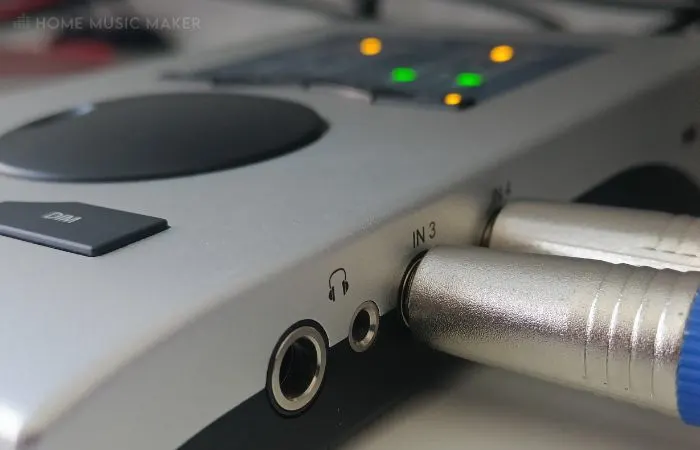

Another consideration is headphone jacks.
If you plan on using headphones, then you will need an audio interface with headphone jacks.
It is common in a home studio to have multiple audio output channels for monitoring via headphones on top of your main speaker system.
7. Built-In Effects
Are you after built-in effects?
You may benefit from an audio interface with built-in effects if you want to use effects such as reverb, delay, or EQ.
And since the effects are happening outside your digital audio workstation, that is one less plugin, which saves CPU (a very valuable and limited recourse in music production).
8. External Power Supply
The penultimate consideration is an external power supply.
Some audio interfaces require an external power supply to function properly. In contrast, others receive power from your computer over the USB cable.
9. Price
The final thing you need to consider is price.
Audio interfaces can range in price from around $50 to over $1000!
You will need to decide how much you are willing to spend on an audio interface and what will be the most beneficial to your specific needs as a music producer.
Related Questions
Does a Mixer Affect Sound Quality?
In general, a mixer will not affect the sound quality of your audio signal. This is because a mixer is simply a device that allows you to control the levels of multiple audio signals at once. It can change the spectral balance with a built-in eq, but not the quality.
Does a High-Quality Audio Interface Make Music Sound Better?
A high-quality audio interface can make music sound better by providing a cleaner signal with less noise and better conversion from digital to analog.
Can You Use an Audio Interface Without A Computer?
Technically you can use an audio interface without a computer. Still, you will need another device to provide the digital signal that the audio interface will convert to an analog signal.
You will also need a way of interfacing with the device, such as USB host functionality.
I suppose you could also probably spin up a solution by communicating over a serial port, but I wouldn’t recommend it unless you really know what you are doing.
Is It Worth It to Upgrade Your Audio Interface?
This will largely depend on your specific needs and the current interface that you are using.
If you are using a very old or entry-level audio interface, then upgrading to a newer and better-quality interface can make a big difference in the overall quality of your recordings.
On the other hand, upgrading may not provide a significant enough improvement to justify the cost if you already use a high-quality audio interface.
Final Words
A few key benefits to using an audio interface in your home studio exist.
Firstly, audio interfaces typically offer much higher-quality audio than your average computer’s built-in sound card.
This means that your recordings will sound better and less likely to suffer distortion or other audio problems.
Secondly, audio interfaces often come with various input and output options, which can be extremely helpful if you want to record multiple instruments or connect to external speakers or other audio equipment.
Finally, audio interfaces typically offer much lower latency than your average soundcard, which can be a huge help when recording and playing back audio in real-time.
Are you looking to upgrade your audio interface? Check out of top 12 sound cards here.

 Want to connect with other music producers for help and guidance?
Want to connect with other music producers for help and guidance?